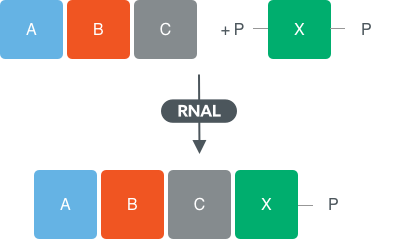
Addition of single nucleotides to form blockmers
Using state-of the-art synthetic biology design, Almac has designed panels of diverse RNA ligases (RNAL) to screen reactions for coupling of a single nucleotide to an oligonucleotide (at least 3 residues in length).
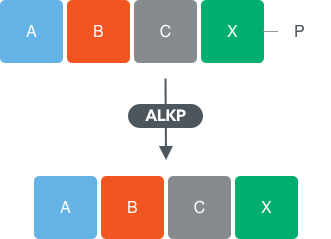
To continue extending the oligonucleotide another enzyme class, alkaline phosphatase (ALKP), can be used to cleave the 3’ phosphate, providing a 5’-hydroxyl which can be used for further RNA ligase extension if desired.

Once the required blockmers are assembled larger strand construction can begin. The RNAL can couple both natural and unnatural nucleotides that have modifications in 2’ position such as o-methyl or fluoro groups as well as incorporation of phosphorothioate linkages.
Using blockmers to build single stranded RNA oligonucleotides
Almac use a template independent approach to link blockmers using our selectAZyme™ RNAL enzyme panel. The enzymes can link fragments that have natural or 2’ modified nucleotides as well as accommodating blockmers with phosphorothioate linkages.
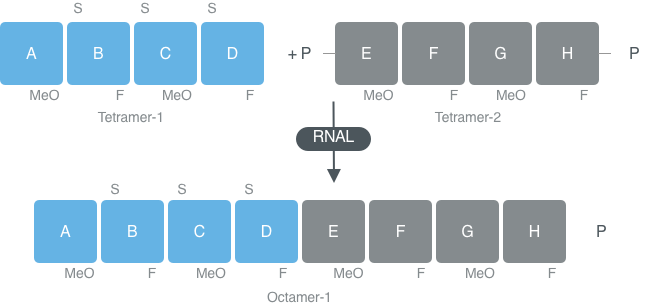

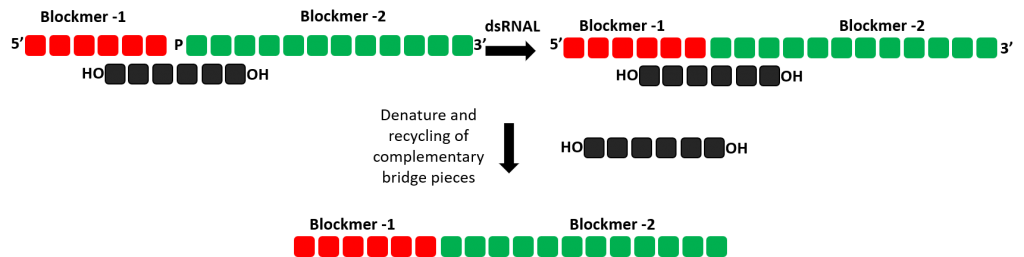
Using double stranded RNAL synthesis to produced single stranded RNA oligonucleotides
Various strategies for constructing the oligonucleotide can be investigated through the use of Almac’s double stranded RNAL within the selectAZyme™ panel. A short complementary bridging sequence can be used to bring two single strands together for ligation with double stranded RNAL potentially providing more favourable conditions for ligation.